




in association with Amazon.com

Woman to Woman:
Your Body and Your Health

Pregnancy: Teen Decisions

Sex: What You Don't
Know Can Kill You
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a general term for a bacterial infection in the female pelvic organs. Specific types of PID include salpingitis (infection of the fallopian tubes), endometritis (infection of the uterine lining), and cophoritis (infection of the ovaries). Most infections are caused by the same organisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhea and chlamydia. Usually PID bacteria enter the vagina during sex and ascend into the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Bacteria may also enter the body after an invasive gynecological procedure.
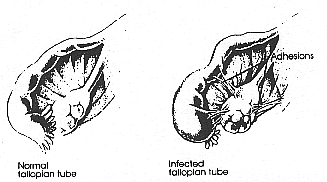
Prompt treatment of PID is important. Infection of the fallopian tubes may lead to scarring and adhesions (bands of scar tissue) that can obstruct the tubes, causing infertility. Over one in twelve women are left infertile after a first episode of PID, one in five are infertile after a second episode, and over 40% are left sterile after three or more episodes of PID. PID is the leading cause of infertility in women. Other problems include chronic recurrances, chronic pain, premature hysterectomy, and depression. At least 10 percent of all sexually active teens are infected with PID.
Symptoms of PID include:
- persistent cramps
- pain during or after sexual intercourse
- temperature of 102-104 degrees F
- unusual vaginal bleeding or foul smelling discharge
- tenderness in the lower abdomen
- chills
- many cases have no symptoms
Risk factors include:
- multiple sex partners
- recent IUD insertion
- sexual activity during adolescence
- use of non-barrier type contraceptives (pill, foam, etc.)
- past history of PID or a sexually transmitted disease
- abortion, childbirth, miscarriage, or other gynecological procedure
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
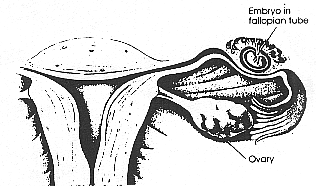
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when the embryo implants outside the uterus. In 95% of cases, the embryo implants in a fallopian tube, which is why this condition is often termed a "tubal pregnancy." Since the fallopian tubes are not large enough to accommodate a growing embryo, the pregnancy cannot continue normally. If identified early, the embryo is removed. In some cases, the embryo grows until the fallopian tube is stretched so much that the tube ruptures. Rupture of the tube is a medical emergency because it can resulting in severe hemorrhaging. An ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening condition.
Symptoms include:
- sudden persistent pain in the lower abdomen, usually to one side
- bleeding and abdominal pain after a missed or light period
- persistent fainting or dizziness (could signal internal bleeding)
Risk factors include:
- previous pelvic infection
- previous ectopic pregnancy (repeat rate is about 12%)
- history of endometriosis
- previous tubal surgery
- one or more surgical abortions
- becoming pregnant with an IUD in place
- becoming pregnant while taking the mini-pill (10% of pregnancies are ectopic)
CERVICAL CANCER
Cervical cancer occurs when cells on the cervix grow in an abnormal way. The human papillomavirus (HPV), the sexually transmitted disease which can cause genital warts, is a precursor to cancer of the cervix. Have regular Pap tests to check for this condition as it can be fatal. When cervical cancer is detected at its earliest stage, the 5-year survival rate is more than 90 percent.Symptoms of cervical cancer:
- abnormal bleeding, such as between periods or after intercourse
- foul smelling vaginal discharge
- discomfort during intercourse
Risk factors include:
- early onset of intercourse: women who begin having sex before age 20 are more vulernable to cell changes
- three or more sexual partners in one's lifetime: the greater the number of sexual partners, the greater the risk of acquiring HPV
- having a male sex partner who has had other partners: especially if a previous partner had cervical cancer
- history of genital warts
- immunosuppressive disorders such as HIV/AIDS
- failure to receive regular Pap test screening
- long term use of oral contraceptives
- smoking
TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a very rare, but potentially serious illness, caused by particular type of bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, which poisons the blood. TSS is most common during the adolescent years, but it can affect males or females at any age. Half of all cases are related to tampon use; the higher the absorbancy, the greater the risk. The other half result from localized infections, for example following burns, boils, insect bites or surgery. TSS is not a contagious disease, but you can get it more than once. It be effectively treated with antibiotics and other medicines, but prompt treatment is essential as about 2.5% of all reported cases are fatal.
Symptoms of TSS:
- sudden, high fever
- vomiting, diarrhea
- dizziness, faintness, weakness
- sore throat, aching muscles and joints
- rash, like a sunburn
- confusion
Risk factors include:
- use of tampons
- recent wound or surgery
- use of barrier methods of contraception (diaphragm, cervical cap, sponge)
- adolescence or young adulthood
If you think you may have any of the conditions listed above, see a doctor right away.
![]()
- At this site
- Sexually Transmitted Disease
- Yeast Infection
- The Best Prevention for Reproductive Tract Conditions
- Proper Condom Use
- The following links are provided as an informational resource or counterpoint and are not necessarily endorsed by the author:
Go to Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sources: Contraceptive Technology by R. Hatcher et al, 17th Revised Ed., 1998; The Pregnancy Place, website by Susan Ackerman; and the Medical Institute for Sexual Health, P. O. Box 4919, Austin, TX, 78765.
